Mechatronics
Mechatronics is the big-strange word that covers so much. The marriage of mechanical, electrical, computer and software skills in order to work with smart technologies, TOOLKIT prepares students for various career pathways within the ever-changing landscape of Mechatronics.
Students learn integrated systems that combine electrical technologies with mechanical technologies and computer programming for real-world skills that directly relate to modern jobs in manufacturing and automation.
Mechatronics sits at the intersection of mechanics, electronics, and computing, and is built on the idea of creating simpler and smarter systems. Toolkit provides the training systems that empower mechatronics technicians and specialists with the skill sets to thrive in contemporary, advanced automated manufacturing industries.
Electro-mechanical technologists and technicians combine knowledge of mechanical technology with knowledge of electrical and electronic circuitry. They operate, test, and maintain unmanned, automated, robotic, and/or electromechanical equipment.
Electro-mechanical and mechatronics technologists and technicians typically do the following:
- Read blueprints, schematics, and diagrams to determine the method and sequence of assembly of a machine or a piece of equipment
- Verify dimensions of parts, using precision measuring instruments
- Operate metalworking machines to make housings, fittings, and fixtures
- Inspect parts for surface defects
- Repair and calibrate hydraulic and pneumatic assemblies
- Use instruments to test the performance of electromechanical assemblies
- Use soldering equipment and hand tools to install electronic parts and hardware
- Operate, test, or maintain robotic equipment
- Analyze and record test results
They install, maintain, and repair automated machinery and computer-controlled mechanical systems in industrial settings, and also test, operate, and/or maintain robotic equipment at worksites. This equipment may include unmanned submarines, aircraft, or similar types of equipment for uses that include oil drilling, deep-ocean exploration, or hazardous-waste removal.
They average pay for someone with these skills is over $61,040.00.
Showing all 2 results
-
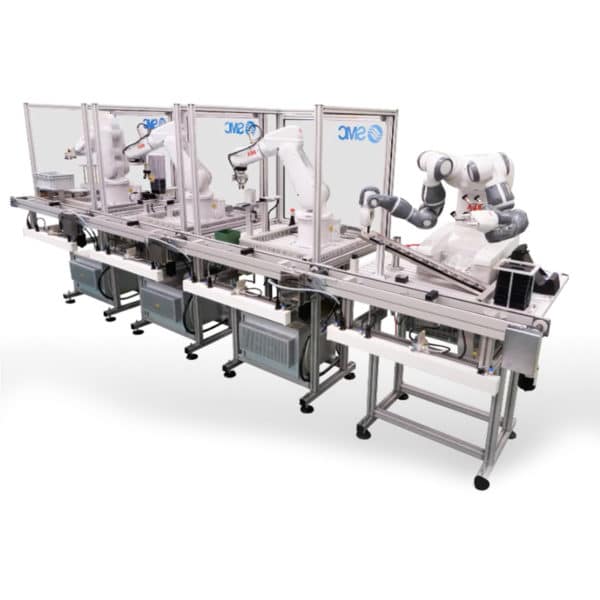
Robotized Assembly System
SMC’s Robotized Assembly Training System, the RAS-400, allows learners to get a real-world look at fully automated assembly environments featuring your choice of industrial robot(s).
This modular robotized assembly system consists of 4 different industrial robot stations forming a flexible automation cell. The process includes an entire series of
- Feeding
- Material handling
- Assembly verification
- Loading operations
All operations are carried out using components from different technologies (pneumatics, vacuum, sensors, etc.) that students will have to understand and apply. The primary training focus of this training system is industrial robotics, including collaborative robots.
-
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assist Systems) Trainer
With the ADAS Trainer, you’ll be teaching the most advanced concepts in vehicle safety and automation. As the automotive industry has evolved, the role of sensors in today’s vehicles has become more important. Unfortunately, these systems can be challenging to understand without hands-on experience, which is why the ADAS Trainer is essential.
This training system breaks down the elements of advanced driver assist systems and autonomous vehicle concepts, providing a clear and concise look at the technologies involved. Thanks to our advanced simulations, students will be able to visualize the data collected by each sensor, as well as where they are located in a vehicle. Then, they’ll be able to analyze that data to understand how each sensor contributes to overall vehicle operation.
The EV-360 ADAS Training System was designed to demonstrate the fundamental concepts and technologies currently incorporated in today’s advanced vehicles.This trainer allows a student to visualize sensor readings and results, literally locating where the components are on a vehicle and compares the strengths and weaknesses of the various sensors and technologies to one another. This trainer is a scale model, providing visual cues to help students recognize design function and orientation.